88Scott Penthouse Collection







WHERE YOU BELONG · The most remarkable address in the heart of downtown Toronto is yours.
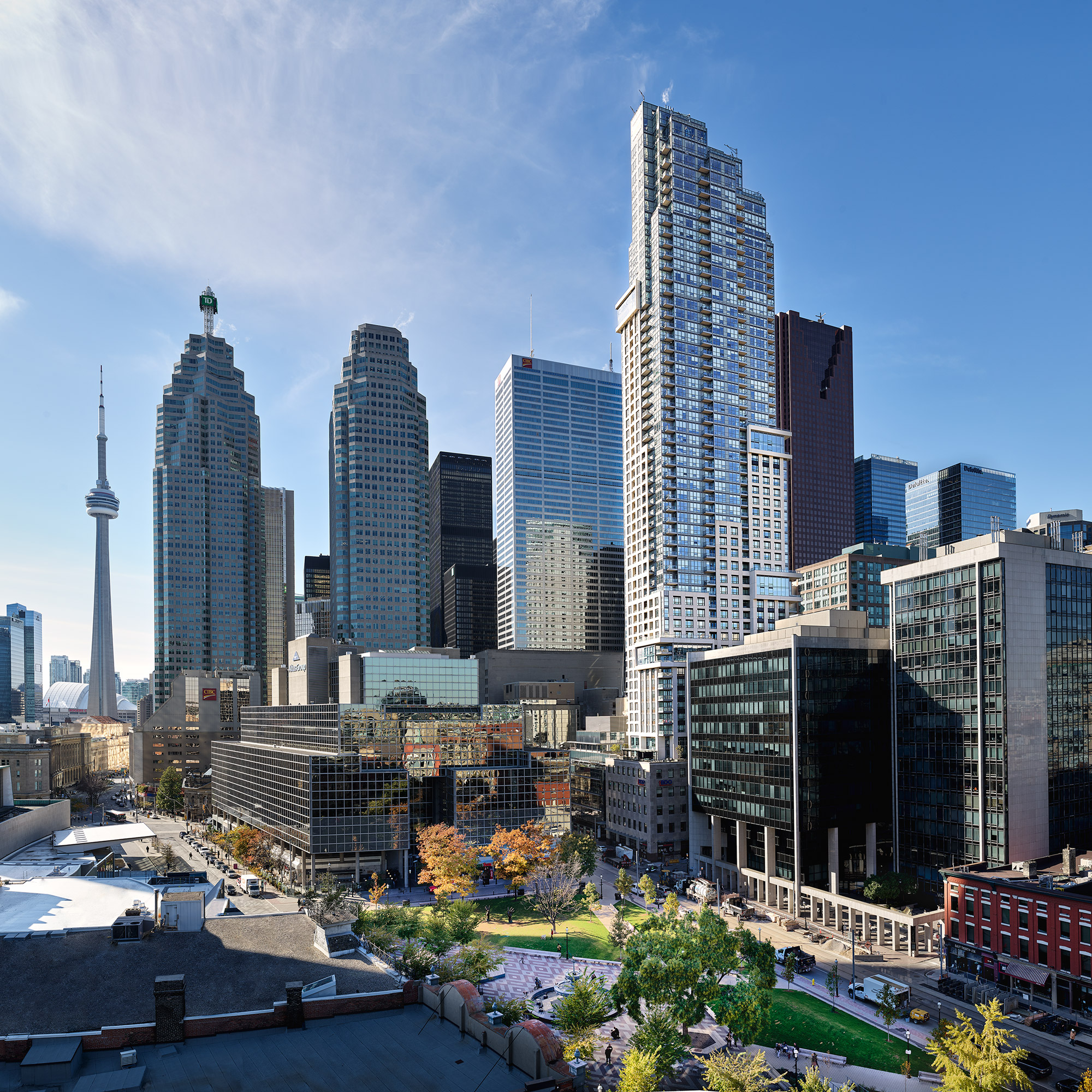


A NEW LANDMARK · Experience contemporary refinement beyond the boundaries of conventional downtown living.

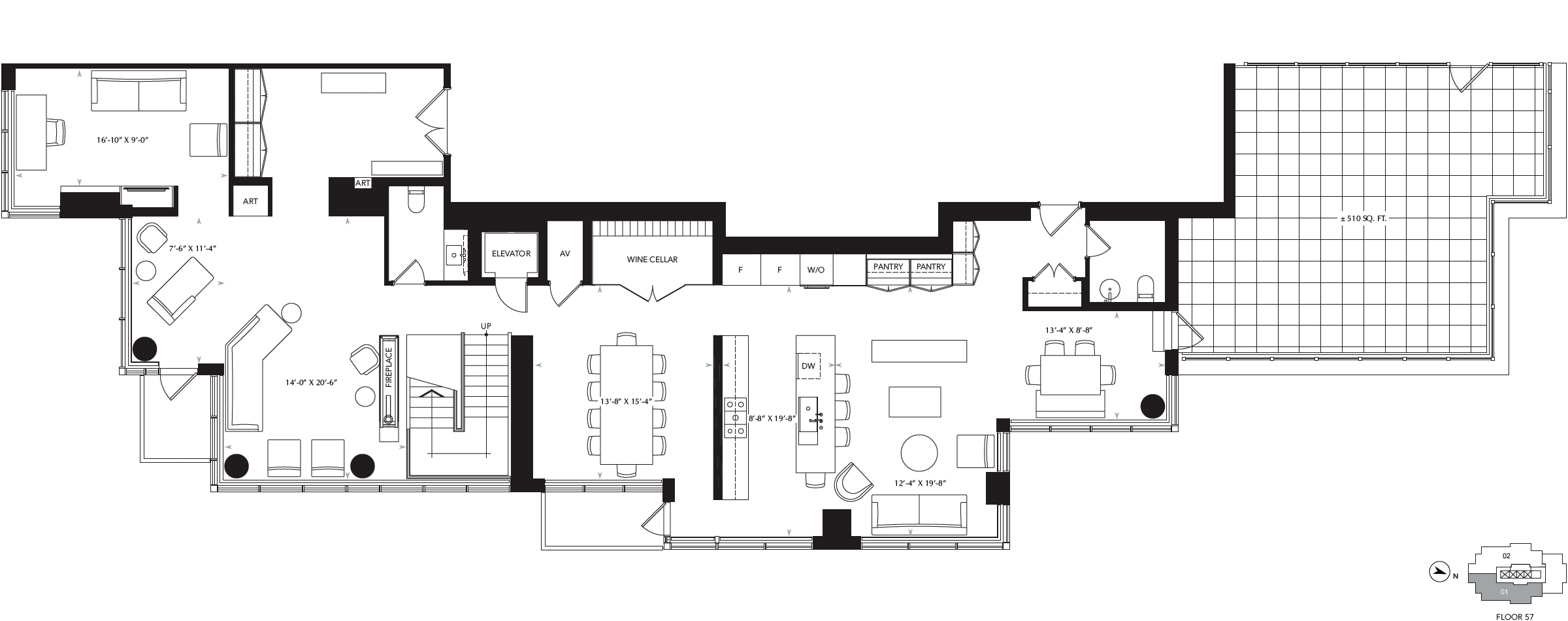
THE SUMMIT OF 88 SCOTT · Discover four brilliantly designed and lavishly finished penthouses wrapped in iconic Toronto views.
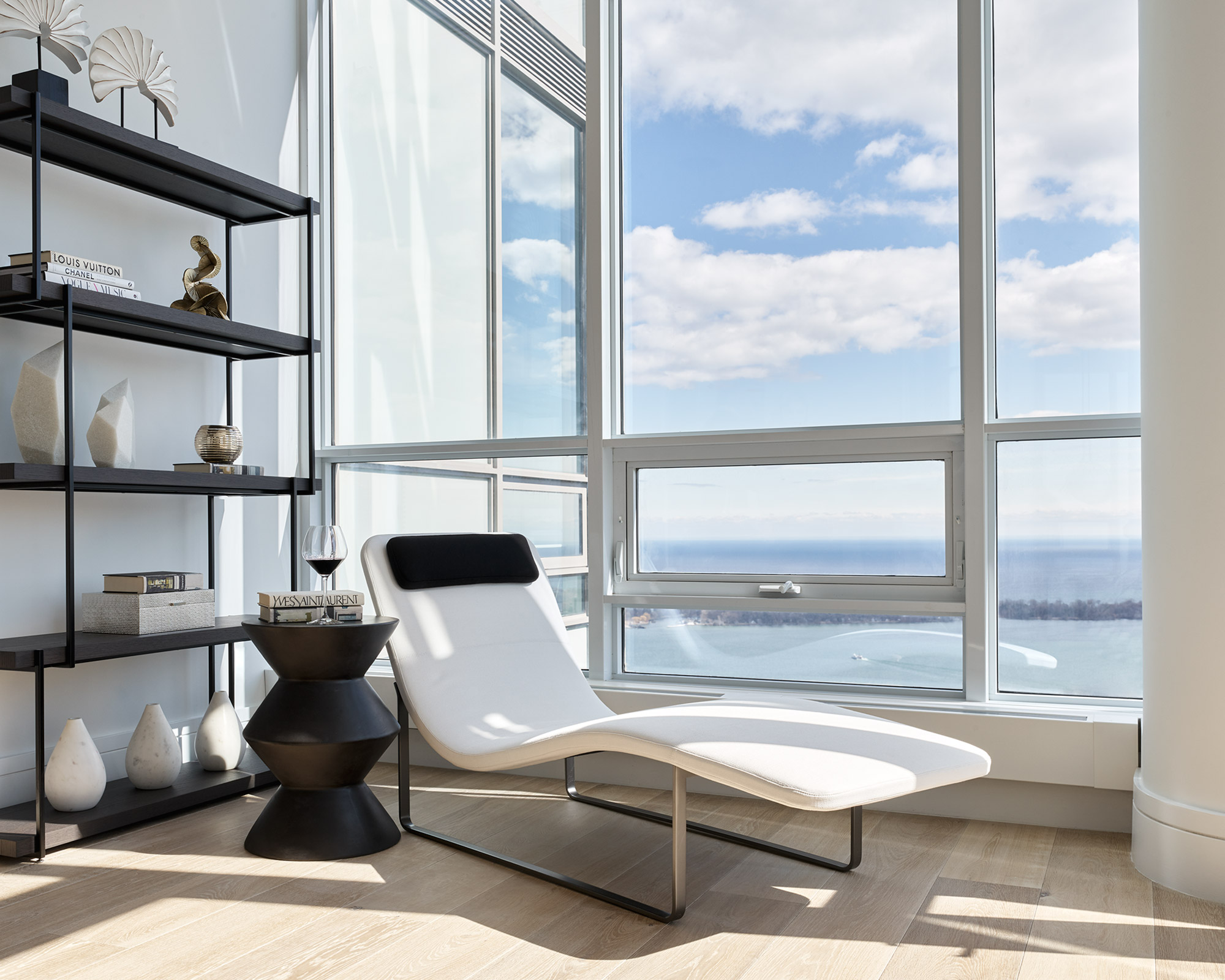

CONCERT. BUILDING A PEOPLE-FIRST FUTURE · Putting people first is at the heart of the Concert story.
